● What Is Thiamine Hydrochloride ?
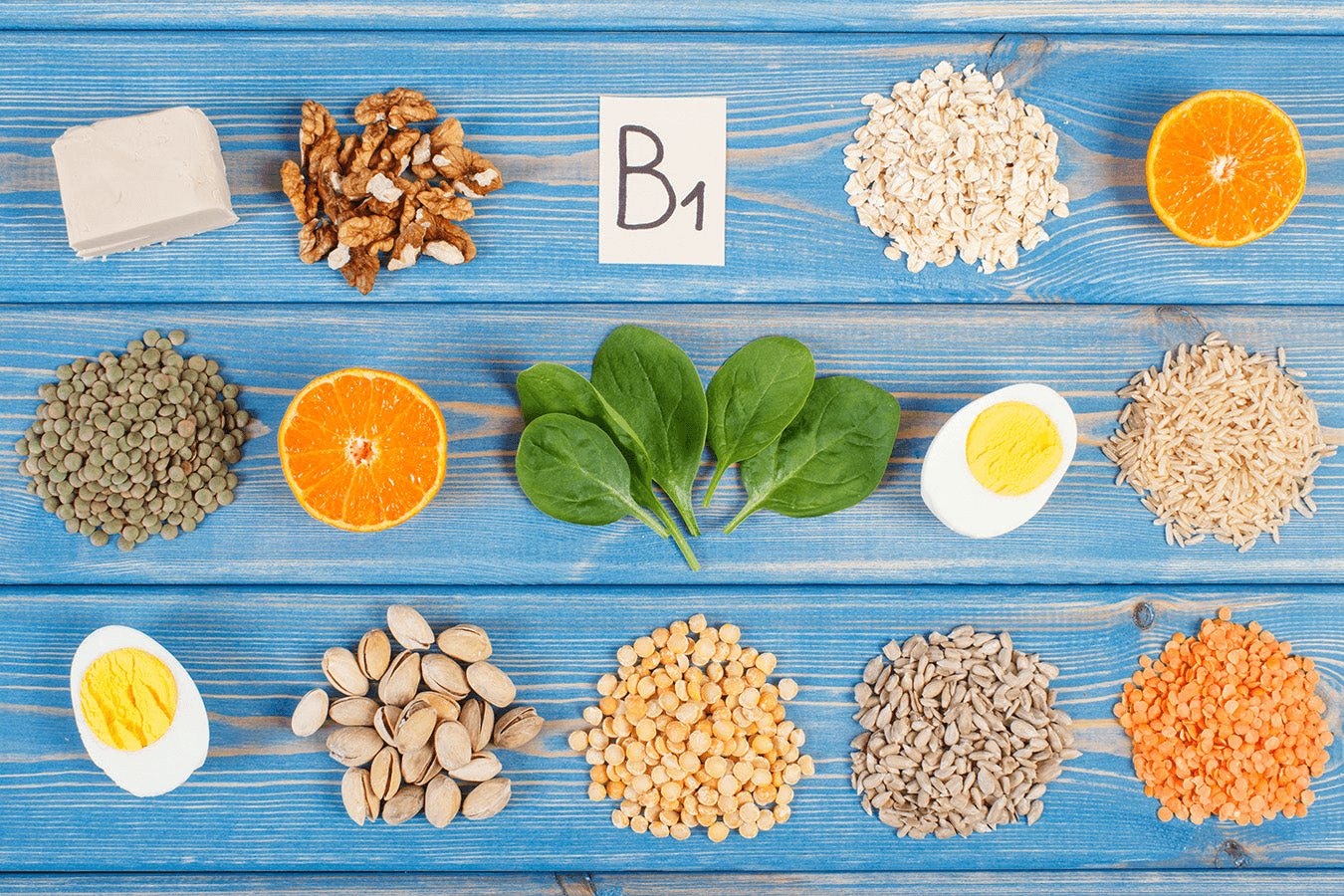
Thiamine hydrochloride is the hydrochloride form of vitamin B₁, with the chemical formula C₁₂H₁₇ClN₄OS·HCl, molecular weight 337.27, and CAS number 67-03-8. It is a white to yellowish-white crystalline powder with a faint rice bran smell and bitter taste. It is easy to absorb moisture in a dry state (it can absorb 4% moisture when exposed to air). The core physical and chemical properties include:
Solubility: Very soluble in water (1g/mL), slightly soluble in ethanol and glycerol, and insoluble in organic solvents such as ether and benzene.
Stability: Stable in an acidic environment (pH 2-4) and can withstand high temperatures of 140°C; but it decomposes rapidly in neutral or alkaline solutions and is easily inactivated by ultraviolet rays or redox agents.
Detection characteristics: It reacts with ferric cyanide to generate a blue fluorescent substance “thiochrome”, which becomes the basis for quantitative analysis38.
The world’s mainstream preparation process is chemical synthesis, which uses acrylonitrile or β-ethoxyethyl propionate as raw materials and is produced through condensation, cyclization, replacement and other steps, with a purity of more than 99%.
● What Are The Benefits Of Thiamine Hydrochloride ?
Thiamine hydrochloride is converted into the active form of thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) in the human body, and plays multiple physiological functions:
1. Energy metabolism core: as a coenzyme of α-ketoacid decarboxylase, it directly participates in the process of glucose conversion to ATP. When it is deficient, it leads to pyruvate accumulation, causing lactic acidosis and energy crisis.
2. Nervous system protection: Maintaining normal conduction of nerve impulses. Severe deficiency causes beriberi, with typical symptoms including peripheral neuritis, muscular atrophy, and heart failure. Historically, it has caused a large-scale epidemic in Asia, killing hundreds of thousands of people annually.
3. Emerging research value:
Myocardial protection: 10μM concentration can antagonize acetaldehyde-induced myocardial cell damage, inhibit caspase-3 activation, and reduce protein carbonyl formation.
Anti-neurodegeneration: In animal experiments, deficiency can lead to abnormal accumulation of β-amyloid protein in the brain, which is related to the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease.
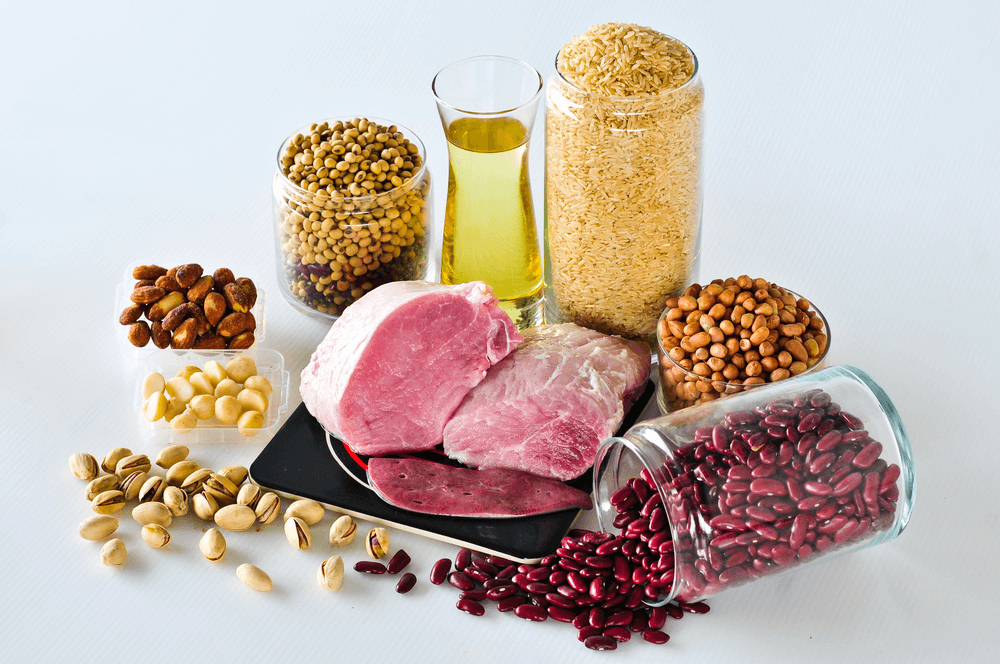
High-risk groups for deficiency include: long-term consumption of refined white rice and flour, alcoholics (ethanol inhibits thiamine absorption), pregnant women, and patients with chronic diarrhea.
● What Are The Application Of Thiamine Hydrochloride ?
1. Food industry (largest share):
Nutrient enhancers: added to cereal products (3-5mg/kg), infant food (4-8mg/kg), and milk drinks (1-2mg/kg) to make up for the loss of nutrients caused by fine processing.
Technical challenges: Because it is easy to decompose in an alkaline environment, derivatives such as thiamine nitrate are often used as substitutes in baked foods.
2. Medical field:
Therapeutic applications: injections are used for emergency treatment of beriberi (neurological/heart failure), and oral preparations are used as auxiliary treatments for neuritis and indigestion.
Combination therapy: combined with magnesium agents to improve the efficacy of Wernicke encephalopathy and reduce the recurrence rate.
3. Agriculture and biotechnology:
Crop disease resistance inducers: 50mM concentration treatment of rice, cucumbers, etc., activates pathogen-related genes (PR genes), and enhances resistance to fungi and viruses.
Feed additives: Improve the efficiency of sugar metabolism in livestock and poultry, especially in heat stress environments (increased demand for sweat excretion).
● NEWGREEN Supply High Quality Thiamine Hydrochloride Powder
Post time: Jun-30-2025