● What Is Enterococcus Faecium ?
Enterococcus Faecium, a resident member of the human and animal intestinal flora, has long been active in microbial research as both an opportunistic pathogen and a probiotic. Its unique physiological characteristics and functional diversity offer broad potential for application in agriculture, healthcare, and environmental management, but the associated risk of drug resistance has also drawn significant scientific attention.
Enterococcus Faecium is a Gram-positive, hydrogen peroxide-negative coccus with a diameter of 0.5-1.0 microns. It lacks spores and a capsule and can form short chains or single colonies. As a representative species of the Enterococcus genus, it is widely distributed in the digestive and reproductive tracts of humans and mammals, as well as in the environment, forming a symbiotic relationship with its host. However, some strains carry virulence genes (such as hemolysins and adhesins) that can cause infection, making it a significant pathogen of nosocomial infections.
● What Are The Benefits Of Enterococcus Faecium ?
1. Prebiotic Function
Barrier Construction: Adhere to the intestinal epithelium to form a biofilm, inhibit the colonization of Escherichia coli and Salmonella, and reduce the levels of intestinal inflammatory factors.
Immunomodulation: Activate macrophages, promote antibody secretion, and enhance host disease resistance.
Nutrient Metabolism: Break down proteins into small peptides, synthesize B vitamins, and promote calcium absorption.
2. Pathogenic Mechanism
Host Protein Hijacking: Binds to the host FABP2 protein via the surface receptor EF3041, activating the quorum sensing pathway and exacerbating the intestinal dysbiosis in Crohn’s disease.
Virulent Expression: In immune-compromised individuals, the virus invades the bloodstream, urine, and other organs, causing endocarditis, urinary tract infections, and postoperative abscesses.
● What Are The Application Of Enterococcus Faecium ?
1. Animal Husbandry
Feed Additive: Add 100-200 grams per ton to improve intestinal microbiome, reduce diarrhea rates, and reduce ammonia nitrogen emissions.
Silage Fermentation: Works synergistically with cellulase to improve feed palatability and nutritional value.
2. Aquaculture
Water Purification: Apply 50-100 grams per mu of enterococcus faecium to degrade ammonia nitrogen and nitrite, inhibiting blue-green algae blooms.
Disease Control: Inhibits aquatic pathogens by secreting antimicrobial peptides, reducing antibiotic reliance.
3. Medical
Probiotic Preparations: Used in vaginal suppositories or oral preparations to regulate bacterial balance (Note: Due to the risk of drug resistance, some countries restrict their medical use).
Drug Resistance Research: Used as a model bacteria to analyze the transmission mechanisms of antibiotic resistance.
● Dosage and Safety Guidelines of Enterococcus Faecium
1. Recommended Dosage
Livestock and Poultry Feed: 150 g/ton during the fattening period, 200-250 g/ton during the weaning period, for 10-15 days.
Aquaculture: 0.5 g/m2 for environmental treatment, repeat every 5-7 days in severely deteriorated areas.
2. Precautions
Avoid mixing with disinfectants or hot water. Store in a cool, dry place.
Medical applications require rigorous assessment of drug resistance. Combination with drugs such as vancomycin is prohibited.
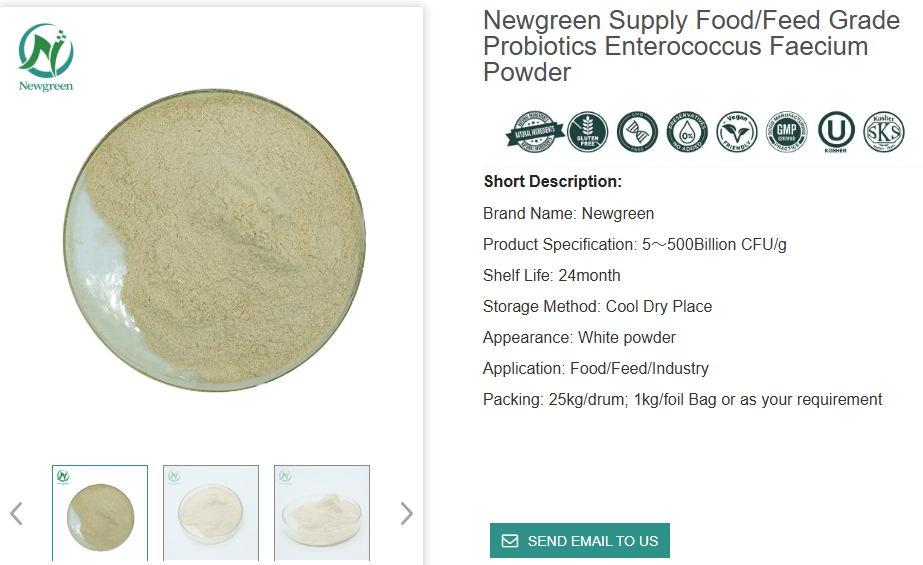
● Newgreen Supply High Quality Enterococcus Faecium Powder
Post time: Aug-14-2025