● What is Bilirubin ?
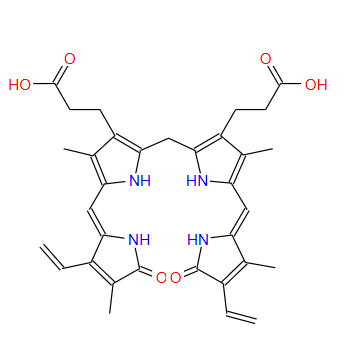
Bilirubin is a product of the decomposition of aging red blood cells. About 2 million red blood cells disintegrate in the spleen every day. The released hemoglobin is enzymatically converted into fat-soluble indirect bilirubin, which is then converted into water-soluble direct bilirubin by the liver and finally discharged into the intestine through bile. Any abnormality in this metabolic chain (such as hemolysis, liver damage or bile duct obstruction) can lead to bilirubin accumulation and cause jaundice.
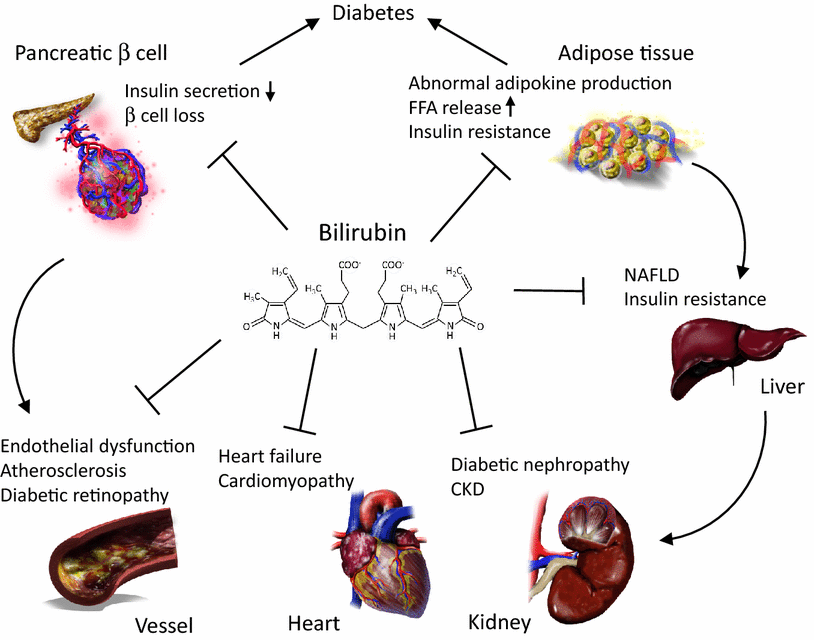
The latest research found that when the bilirubin concentration is ≥17.05 μmol/L, the association between diabetes and stroke can be blocked, and the risk of stroke in male diabetic patients is reduced by 2.67 times. The mechanism is to inhibit high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and systemic immune inflammation index, putting the brakes on the “inflammatory storm”.
Bilirubin is extracted from pig and shark liver, cattle gallbladder and brainstem. We have achieved breakthroughs through technological innovation:
Supercritical CO₂ extraction: retain active ingredients under low temperature environment, avoid solvent residue, and increase purity to more than 98%;
Biological enzymatic hydrolysis process: directional conversion of bilirubin glycosides into active aglycones, increasing bioavailability by 50%.
● What are the benefits of the Bilirubin ?
1. Antioxidant protection
Bilirubin is an important endogenous antioxidant in the body, which can effectively neutralize free radicals (such as superoxide and hydrogen peroxide) and reduce the damage of oxidative stress to cell membranes, proteins and DNA. Studies have shown that low concentrations of bilirubin can enhance the cell’s defense against oxidative damage by activating antioxidant signaling pathways (such as the Nrf2 pathway), and may even reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and neurodegenerative diseases.
2. Immunomodulatory function
Bilirubin can regulate immune responses by inhibiting the release of inflammatory factors (such as TNF-α and IL-6). It can reduce the damage to tissues caused by excessive inflammation while maintaining the balance of the immune system. For example, mildly elevated bilirubin in physiological jaundice of newborns may help reduce the risk of infection through this mechanism. However, excessive concentrations can inhibit the activity of immune cells and increase susceptibility to infection.
3. Cell and neuroprotection
Bilirubin has a special protective effect on the nervous system. It can cross the blood-brain barrier and protect neurons from ischemia or degenerative lesions by inhibiting glutamate excitotoxicity and reducing oxidative damage. In addition, bilirubin can also reduce the damage of liver cells, myocardial cells, etc. under hypoxia or toxin exposure, and maintain organ function.
4. Promote metabolism and excretion cycle
The metabolic process of bilirubin is a key link in the recycling of hemoglobin in the body. After the hemoglobin in aging red blood cells is decomposed into bilirubin, it needs to be combined by the liver and discharged into the intestine with bile. Intestinal bacteria convert it into urobilinogen, part of which is reabsorbed (enterohepatic circulation), and the rest is excreted with feces. This cycle not only helps to remove metabolic waste, but also interacts with intestinal flora to affect the overall metabolic balance.
5. Harm of abnormal levels
Excessive bilirubin: It may cause jaundice (yellowing of the skin and sclera), which is common in hepatitis, biliary obstruction or hemolytic diseases. When free bilirubin is too high, it can pass through the blood-brain barrier and cause neonatal kernicterus (brain damage).
Too low bilirubin: Recent studies have found that mild increases in bilirubin may have a protective effect, while too low levels may be associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and autoimmune disease, but the specific mechanism still needs to be studied.
● What Are The Medical Application Expansion Of Bilirubin ?
1. Core pharmaceutical raw materials
Bilirubin is the main component of artificial bezoar and is used in more than 130 drugs, such as cardiovascular and cerebrovascular drugs (85% effective in relieving coronary heart disease) and menopausal regulation preparations.
2. Nano preparations (BRNPs)
Through nanocarrier technology, the efficacy and targeting of bilirubin have been greatly improved:
Acute gastric ulcer: chitosan-bilirubin (CS-BR), inhibits the secretion of inflammatory factors and promotes mucosal regeneration
Non-alcoholic fatty liver: polyethylene glycol-bilirubin (PEG-BR), reduces liver fat accumulation by 30%, and reduces triglycerides by 40%
Psoriasis: hydrogel-bilirubin, improves skin lesions, without the systemic toxicity of corticosteroids
Stroke: TRPM2 channel inhibitor A23, blocks bilirubin neurotoxicity and reduces infarct size.
Other applications of bilirubin: animal husbandry, environmental protection and functional products
Aquaculture: Adding 4% bilirubin to feed doubles the production of white shrimp and increases the weight gain of carp by 155.1%;
Functional food: Anti-glycation oral liquid, combined with the antioxidant properties of bilirubin to delay skin aging.
● NEWGREEN Supply Bilirubin Powder
Post time: Jun-09-2025